
#How find dns servers mac mac os
Additionally, you may need to quit and relaunch some applications for the DNS changes to carry over to them.Īdvanced Mac users can also adjust DNS from the command line in Mac OS X, though that approach is obviously a bit more technical than simply changing the settings through the Network preference panel. Mac users can clear DNS caches in OS X El Capitan and newer with this command, and for specific Yosemite versions with this command, and even earlier releases of OS X with this. In the screen shot examples above, Google DNS servers (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) are placed above the OpenDNS servers, both of which are faster than ISP provided DNS servers as determined by NameBench for this network environment.ĭepending on what you’re doing and why you’re modifying DNS settings, you may wish to flush DNS cache for the changes to take effect, this is particularly true with editing the hosts file. The topmost DNS servers will be accessed first, so you’ll want to put the best performing servers near the top of the list for best results.
#How find dns servers mac plus
#How find dns servers mac mac os x
This is easily accomplished in MacOS and Mac OS X as we’ll detail in this walkthrough.Īdding, Editing, & Adjusting DNS Server Settings in Mac OS X tcpdump command analyzes network behavior, performance and applications that generate or receive network traffic including dns traffic.While most internet server providers offer their own DNS servers, and most Macs will use DNS from DHCP or a wi-fi router, Mac users sometimes wish to change DNS settings themselves to custom servers, perhaps for better performance, or for troubleshooting purposes. tcpdump command works on most Unix-like operating systems. You can use the tcpdump command to dump traffic on a network and view dns traffic. (Fig.04: 10.0.80.11 and 10.0.80.12 are my DNS server IP address assigned under Unix like operating systems) Method #4: Dump and view traffic on a network (recommended for advanced users only) Hence, type the bat/ cat/ more or less command:

It was passed on to you by your modem / router. However, a better approach is to go through /etc/nf file to see assigned dns server address to your computer. So 10.0.10.11 is my DNS server IP address on Linux, Unix or macOS/*BSD based systems.
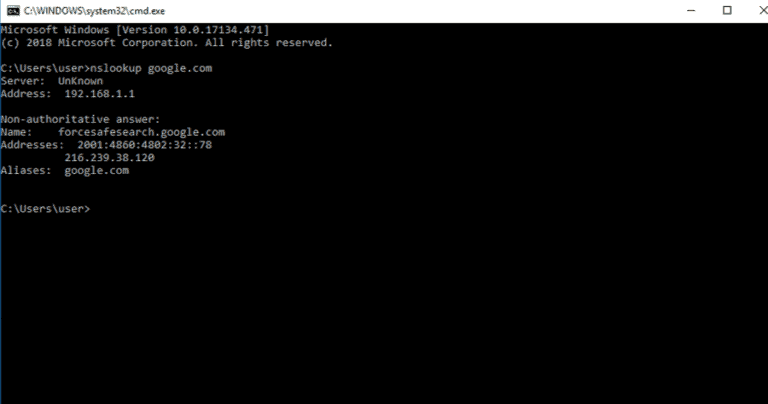
OR use the dig command along with the grep command: Sample outputs: Received 229 bytes from 10.0.10.11#53 in 0 ms Open the terminal application and then type the following host command along with the grep command: Open the bash shell prompt and type the dig or host commands. Method #3: Apple OS X or Unix / Linux Commands This one is used by my computer, and it was passed on to my computer by ISP modem / router. In this example my DNS server is located at 192.168.1.2.

Fig.03: MS-Windows command to find out DNS server IP addresses


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
